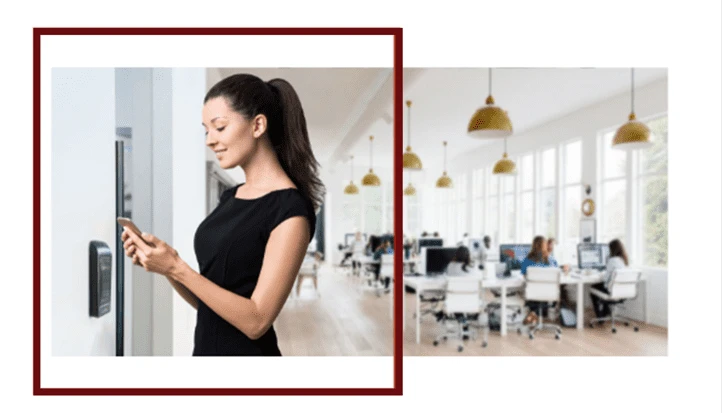
My Teenagers Always Forget Their Keys—Now I Can Unlock the Door Remotely. Does This Sound Familiar?

As a parent, few things are as exasperating as getting that text from your teenager: “I forgot my keys again!” Whether they’re coming home from school, practice, or a night out with friends, it seems like forgetting their house keys has become a regular occurrence. But in today’s tech-savvy world, there’s a solution that brings peace of mind to parents everywhere—remote door access via smartphone. If your teenagers are always forgetting their keys, you’re not alone. Let’s explore how remote access can simplify your life and keep your family secure. The Age-Old Problem of Forgotten Keys Teenagers have a lot on their plates—school, social lives, extracurricular activities—and keeping track of a small item like a house key isn’t always top of mind. In fact, research shows that teenagers are prone to losing things, with keys being one of the most commonly misplaced items. This can lead to stress, inconvenience, and sometimes even risky situations as your teens are left locked out, waiting for someone to come home. A Modern Solution: Remote Door Access Fortunately, modern technology has a solution. With a smart lock system connected to your smartphone, you can unlock the door for your teenagers from anywhere. Whether you’re at work, running errands, or even out of town, remote access ensures that your teens can safely and easily get inside, no matter what. The Benefits of Going Keyless Convenience: No more frantic texts or calls. With just a tap on your phone, you can let your teens in instantly, providing them with the security of home, even when they’ve forgotten their keys. Peace of Mind: Knowing you can always grant access to your home reduces the stress of lost keys and eliminates the need to hide spares around the house—a practice that can compromise security. Enhanced Security: Many smart locks offer additional features such as access logs, so you can see who entered and when, giving you better oversight of home security. Flexibility: You can easily grant temporary access to babysitters, relatives, or trusted friends without needing to hand out physical keys. You can even control when and for how long access is allowed. Why It’s Worth the Investment While traditional locks have their place, the convenience and enhanced security of remote access are hard to beat, especially for families with busy teenagers. This technology offers a seamless way to manage home security while adapting to the unpredictability of teenage life. Plus, the peace of mind that comes from knowing your teen is safe at home is invaluable. Conclusion If you’re tired of those “I forgot my keys” messages from your teenagers, it might be time to consider upgrading to a smart lock system with remote access. It’s a small investment that can make a significant impact on your daily life, offering both convenience and security. After all, if your teenagers are anything like mine, this could be the solution you’ve been waiting for. Millennium UMC (Ultra Mobile Connect) is an advanced mobile access solution that allows users to seamlessly control and manage their security systems from anywhere using their smartphone, providing unparalleled convenience, enhanced security, and real-time access at their fingertips. Ready to simplify your life and enhance your home security?
Enhancing School Security: How to Manage Hundreds of Visitors Without Compromising Safety

As schools welcome students back for the new academic year, the challenge of managing visitors—everyone from parents and contractors to volunteers and guests—becomes increasingly significant. Ensuring that only authorized individuals can access school premises is crucial for maintaining a safe environment. But how can schools manage hundreds of visitors daily without compromising security? Understanding the Need for Visitor Management Systems A comprehensive Visitor Management System (VMS) serves as a school’s first line of defense, transforming every visitor into a verified guest. These systems not only track who is entering the school but also manage access in a way that enhances overall security. According to a recent study by the National Center for Education Statistics, 63% of public schools now use visitor management systems to track and manage visitors, reflecting a growing recognition of their importance. How Visitor Management Systems Work Visitor Management Systems work by scanning identification, verifying credentials, and issuing badges that clearly indicate the visitor’s identity and purpose on campus. These badges can be customized to reflect different groups of visitors, such as parents, contractors, or delivery personnel. The system can also restrict access based on time—issuing badges that are valid for only a day, an hour, or even limiting access to specific areas within the school. This ensures that visitors are not only identified but also monitored and controlled throughout their time on campus. Integration with Other Security Measures Visitor Management Systems can seamlessly integrate with other access control measures like Millennium’s mobile connect solutions, door locks, and surveillance cameras. This creates a comprehensive security network that further protects the school community by ensuring that all aspects of security are interconnected and responsive to real-time data. Conclusion In today’s educational landscape, ensuring the safety of students and staff is more important than ever. With a robust Visitor Management System, schools can effectively manage the influx of visitors while maintaining a secure environment. Millennium’s Visitor Management solutions are designed to enhance school safety by providing comprehensive visitor tracking and access control options. Millennium’s access control provides schools with a comprehensive system to track and manage visitors in real-time, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access secure areas, keeping your campus safe and secure at all times. Ready to enhance your school’s security and manage visitors more effectively? Contact Millennium today to learn more or request a free demo of our Visitor Management solutions. Let’s make safety a top priority this school year!
Florida School Safety Commission Wants Clarification of New Door Lock Rules

The Florida School Safety Commission has recently taken the lead by calling for greater clarity regarding new door lock regulations for educational institutions. This proactive move underscores the critical role of access control in ensuring student safety. As Florida sets an example, schools across the nation are encouraged to follow suit as they prepare for the 2024-2025 academic year. Understanding and implementing effective access control measures is essential for protecting students, staff, and the integrity of educational environments. Addressing Security Challenges in Schools The need for enhanced security measures in schools has never been more apparent. Modern access control solutions can help schools manage who enters and exits their buildings, providing peace of mind for parents, students, and staff alike. Understanding the New Door Lock Regulations The new door lock rules are designed to ensure that all classrooms and critical areas within schools can be quickly and easily secured in an emergency. However, these regulations have raised several questions regarding implementation, compatibility with existing systems, and overall effectiveness. The Florida School Safety Commission is seeking detailed guidelines to help schools comply with these regulations without compromising safety or incurring excessive costs. Implementing Effective Access Control Solutions 1. Integrated Access Control Systems To meet the new regulations, schools should consider integrated access control systems that combine physical locks with digital management tools. These systems can control who has access to various parts of the school, track entry and exit times, and provide real-time alerts in case of unauthorized access attempts. 2. Scalable and Customizable Solutions Schools vary greatly in size and layout, requiring access control solutions that are both scalable and customizable. Systems should be able to grow with the school’s needs and adapt to different building configurations. Open systems that integrate with other security measures, such as surveillance cameras and emergency communication tools, offer the most flexibility and long-term value. 3. User-Friendly Technologies The latest access control technologies, including biometric authentication and mobile credentials, provide enhanced security and convenience. Biometric systems, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, ensure that only authorized individuals can access secure areas. Mobile credentials, which allow access via smartphones, are particularly useful for staff and students who are already accustomed to using mobile devices in their daily lives. Real-World Applications and Success Stories Schools across the country are already benefiting from advanced access control solutions. For example, a recent case study highlighted how a high school in Texas successfully implemented a comprehensive access control system. This system not only improved security but also streamlined daily operations, such as attendance tracking and visitor management. The school reported a significant decrease in unauthorized access incidents and an overall improvement in safety and efficiency. Conclusion As the Florida School Safety Commission works to clarify the new door lock regulations, schools must proactively seek out and implement effective access control solutions. By integrating physical and digital security measures, choosing scalable and user-friendly technologies, and learning from successful implementations, schools can create safer environments for students and staff. Millennium Group’s advanced access control systems are designed to meet these needs, offering the flexibility, security, and peace of mind required in today’s educational landscape. Millennium Group’s solutions go beyond traditional access control. Our systems allow for remote control of doors, ensuring that access can be managed from any location, which is crucial in emergency situations. Sensitive areas within the school can be protected using geofencing technology, which restricts access based on geographic locations. Facial recognition technology adds an additional layer of security, ensuring that only authorized individuals can enter specific areas. This technology not only enhances security but also simplifies the process of managing and monitoring access across the campus. As Florida schools lead by example, it’s time for others to follow. Contact Millennium Group today to learn more about our access control solutions and how we can help you comply with new regulations while ensuring the safety of your students and staff.
Enhancing Access Control with Facial Recognition for Highly Secure Spaces.

In the realm of access control for highly secure spaces, such as bank vaults, laboratories, data centers, and government facilities, the need for advanced security measures is paramount. Traditional access methods like keys or keycards are no longer sufficient to safeguard these critical environments. This is where facial recognition technology emerges as a cutting-edge solution, revolutionizing access control with its accuracy, efficiency, and reliability. Let’s explore how facial recognition enhances security in highly secure spaces and examine specific examples like bank vaults, laboratories, and data centers. The Evolution of Access Control Access control systems have evolved significantly, transitioning from mechanical locks to digital solutions that leverage biometric technologies like facial recognition. Facial recognition stands out as a game-changing innovation, offering a seamless and robust method to authenticate individuals based on unique facial features. Enhancing Security in Bank Vaults Bank vaults house valuable assets and confidential information, requiring the highest level of security. Facial recognition technology ensures that only authorized personnel gain access to these restricted areas. Employees and security personnel can be swiftly verified through facial recognition at vault entrances, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Securing Laboratories with Facial Recognition Laboratories handling sensitive research and experiments rely on stringent access control measures. Facial recognition systems provide a secure and efficient way to manage access, maintaining a detailed record of personnel movement within the facility. Researchers can focus on their work with confidence, knowing that access to critical areas is closely monitored and controlled. Protecting Data Centers Data centers store vast amounts of critical information, making them prime targets for cyber threats. Access control is crucial to prevent unauthorized entry and protect sensitive data. Facial recognition technology enhances data center security by ensuring that only authorized personnel can access server rooms and control areas. This mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized tampering. Advantages of Facial Recognition in Highly Secure Spaces. High Accuracy: Facial recognition systems accurately identify individuals based on unique facial features, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Streamlined Access: Employees can enter secure areas without the need for physical keys or access cards, enhancing convenience and efficiency. Real-time Monitoring: Facial recognition systems maintain detailed access logs, enabling real-time monitoring of personnel movement for enhanced security and accountability. Integration with Existing Systems: Facial recognition seamlessly integrates with existing access control systems, providing a scalable solution for highly secure spaces. Implementing Facial Recognition with Millennium Access Control Millennium Access Control specializes in deploying facial recognition technology for highly secure spaces. By partnering with Millennium, organizations benefit from: Expert Consultation: Millennium offers expert guidance on implementing facial recognition systems tailored to specific security requirements. Customized Solutions: Each deployment is customized to align with the unique needs and challenges of bank vaults, laboratories, data centers, and government facilities. Advanced Security Features: Millennium integrates advanced security features to enhance access control and protect highly sensitive areas. Conclusion Facial recognition technology is a transformative solution for enhancing access control in highly secure spaces. By leveraging this innovative technology, organizations can fortify security measures, streamline access, and ensure the protection of valuable assets and information. With the expertise of Millennium Access Control, implementing facial recognition becomes a seamless process, empowering organizations to safeguard their most critical environments with confidence. MGI is a scalable, hosted, access control platform that services any type of real estate. Our cloud-based solution allows managers and tenants to efficiently manage their physical security from anywhere while enhancing the experience and driving profitability.
Top Access Control Trends for 2025
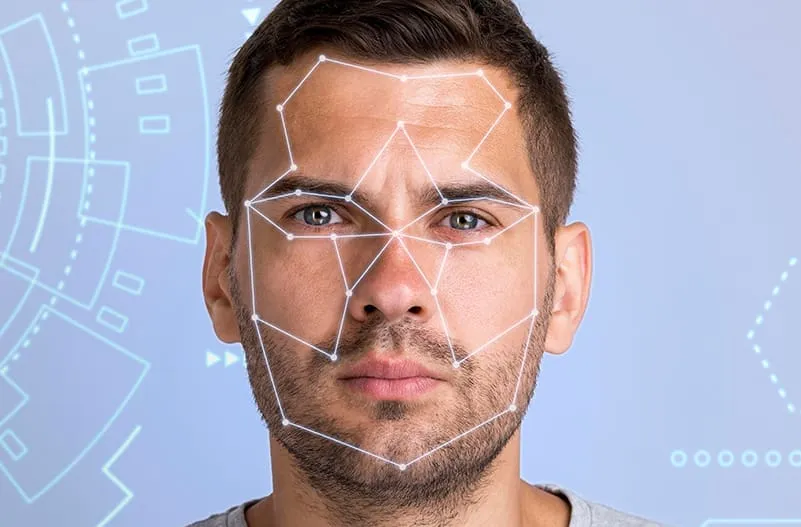

Updated on December 20, 2024 Access control trends 2025 showcase groundbreaking innovations that prioritize user-friendly experiences, robust integrations, and advanced operational capabilities. As technology continues to evolve, organizations must consider how these trends can elevate their security systems. Let’s explore how access control is transforming in 2025 and what organizations should consider enhancing their security strategies. Cloud-Based Access Control Systems: Centralized and Scalable Cloud-based access control systems are rapidly becoming essential and will become the top access control trend in 2025. These systems offer centralized management for security teams, making it easier to handle multiple sites from one platform. By moving to the cloud, businesses can unify control over access credentials, monitor system health, and manage configurations remotely. The scalability of cloud-based solutions allows businesses to expand their security infrastructure without significant hardware investments. As organizations grow, they can easily add more sites or users without overhauling the entire system. Additionally, cloud solutions offer cost-effective disaster recovery and simplified software updates, ensuring that organizations stay up to date with the latest security features without disrupting operations. This cloud-centric model reduces reliance on physical hardware, saving space, and improving operational efficiency. It also enables security teams to streamline data sharing, enhance collaboration, and quickly implement changes across various sites. For businesses with multiple offices or facilities, the centralized nature of cloud access control helps ensure that security is never compromised, even as operations expand. Mobile and Contactless Access: A Seamless User Experience Mobile-based access continues to replace traditional credentials like keycards and fobs, and this access control trend is only set to grow in 2025. The shift to mobile and contactless access provides a more secure and user-friendly experience. Employees, visitors, and contractors can use their smartphones or wearable devices for seamless entry into secure areas, eliminating the need for physical cards and reducing the chances of lost or stolen credentials. By leveraging technologies like Bluetooth, NFC, and QR codes, mobile access solutions ensure fast, reliable, and secure entry. Customizable mobile credentials also allow organizations to integrate visual identity features—such as job titles, department designations, or photos—into the access system, enhancing both security and user experience. Mobile credentials are more than just a convenience; they represent a significant leap forward in access control technology. The security features embedded in smartphones, such as biometric authentication, encryption, and secure communication channels, make mobile access a safer option compared to traditional physical cards. With the ability to remotely deactivate or update credentials, mobile-based access control provides organizations with flexibility and peace of mind. So, don’t be surprised if this solution becomes the top access control trend in 2025. Touchless Technology: Enhancing Hygiene and Efficiency The growing demand for touchless access solutions has been a game-changer, particularly due to the heightened focus on hygiene and reducing physical contact in the wake of the global pandemic. Touchless systems, which often rely on motion sensors, facial recognition, or mobile credentials, offer a modern and hygienic way to navigate buildings without the need to touch any surfaces. These technologies not only improve hygiene but also reduce wear and tear on physical hardware. As more users interact with access systems, devices are subjected to frequent use and potential damage. Touchless technology extends the lifespan of devices by reducing the frequency of contact and minimizing physical strain. This results in fewer maintenance needs and cost savings in the long run. As organizations focus more on the well-being of their employees and visitors, touchless systems become a significant part of the access control landscape. They enhance the overall user experience by making entry faster and more convenient while promoting a safer, cleaner environment. Smart Automation: Streamlining Operations The next in the access control trends list is Automation. By integrating access control systems with building management platforms, businesses can automate a wide range of processes, such as locking schedules, occupancy monitoring, and visitor registration. Automated systems reduce the manual effort involved in managing security tasks and provide a more efficient approach to operational management. For example, in an emergency scenario, automated lockdown protocols can trigger swift and coordinated responses across multiple locations. This ensures that all entry points are secured immediately, and relevant authorities are notified, without requiring manual intervention. Similarly, automated systems can adjust access privileges for users based on factors like location, time of day, or security risk level, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access specific areas at appropriate times. Smart automation enhances operational efficiency by eliminating the need for time-consuming administrative tasks and improving security coverage. With automation, organizations can focus on higher-priority security concerns, knowing that routine tasks are being handled automatically. Video-Integrated Access Control: Enhanced Situational Awareness Video-integrated access control systems are rapidly gaining traction and will continue to do so in 2025, combining access control and video surveillance for a more comprehensive security solution. This integration allows security teams to view real-time video footage in conjunction with access events, providing instant visual verification of an entry attempt. By combining video data with access control logs, security personnel can quickly assess whether an entry was legitimate or if an alert needs to be raised. This integration also makes it easier to review incidents and conduct investigations. Video surveillance systems can be integrated with cloud storage solutions, allowing for easy access to recorded footage from anywhere. The ability to monitor both video and access events from a single platform enhances situational awareness, improves incident response times, and helps organizations make better security decisions. Video-integrated access control enables a holistic approach to security, making it easier to protect assets and personnel while optimizing security operations. This makes it as one of the top access control trends for 2025 Remote Management: A Flexible Security Solution Remote management is a critical cornerstone of modern access control trends for 2025. With an increasingly hybrid workforce, businesses need systems that enable administrators to oversee and manage security operations from anywhere. This access control trend supports hybrid work environments by providing the flexibility to monitor and update credentials, manage incidents, and
A Complete Guide to Parking Access Control System
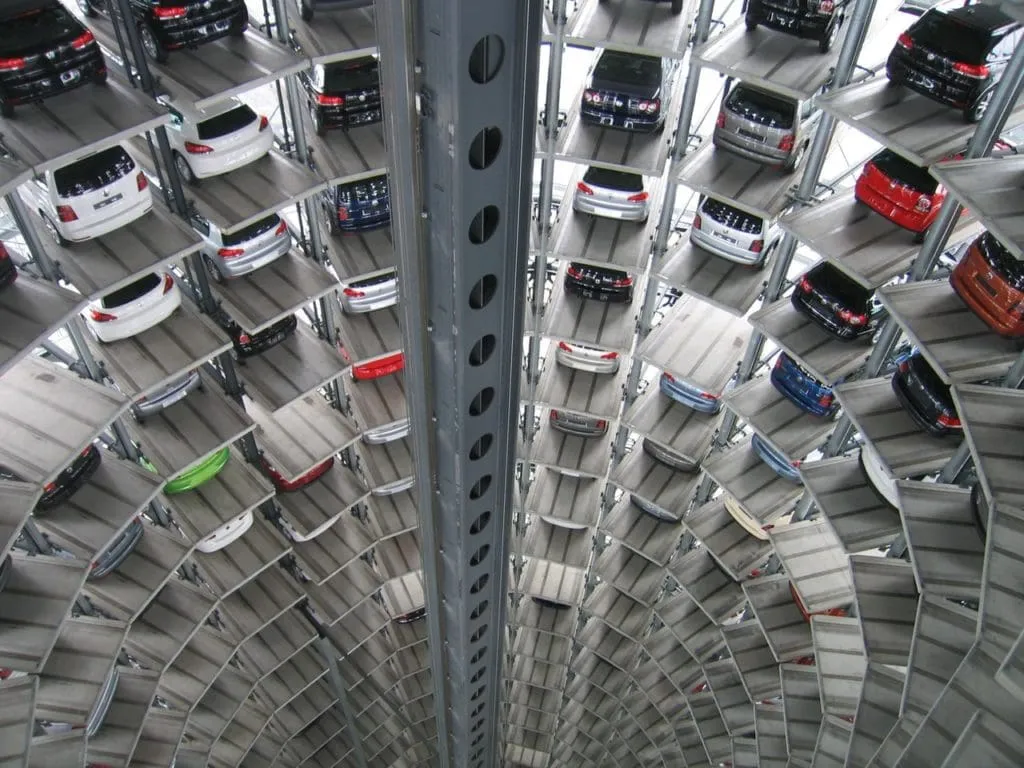

Updated on December 9, 2024 Managing parking facilities is a complex task, requiring efficient systems to regulate the influx and outflux of vehicles while ensuring security and ease of access for users. Parking access control systems, ranging from manual management to fully automated solutions, are designed to address these challenges effectively. This comprehensive guide explores key aspects of parking access control systems, their benefits, and various technologies that have transformed parking management in recent years. What is an Automated Parking Lot Access Control System? An automated parking lot access control system is a solution that enables facility owners to manage parking operations efficiently, restrict unauthorized access, and generate revenue. These systems rely on a combination of physical access control mechanisms, credential management, and integrated payment solutions. Automation introduces significant advantages, such as reducing operational costs, enhancing security, and improving user experiences. Automated parking systems typically use ticketing machines with barcodes, QR codes, or magnetic strips, paired with software for seamless tracking and management. Whether through fully automated systems or hybrid solutions incorporating human oversight, automation ensures a safe, efficient, and user-friendly parking experience. Types of Parking Lot Access Control Systems Key/Remote Access This traditional system works well for long-term users but presents challenges for short-term users. The potential for key loss and unauthorized use makes it less secure compared to modern solutions. Keycard or Key Tag Access Similar to key-based systems, keycards offer enhanced security by allowing administrators to deactivate lost or stolen cards. This method is suitable for both permanent and mid-term users, especially in commercial settings. Keypad Entry Keypads grant access using personalized or general codes. Their flexibility and ease of installation make them a popular choice for short-term users, such as visitors to residential complexes or offices. Codes can be programmed for limited time use and deactivated as needed. License Plate Recognition (LPR) LPR technology uses cameras to read and verify license plates, allowing seamless entry for registered vehicles. This method eliminates the need for physical credentials and simplifies tracking time spent in the facility. Phone Number Recognition Users call a designated number to trigger gate access, ensuring only verified individuals gain entry. This system works well for all types of users, from short-term visitors to long-term tenants. Mobile App or Mobile-Based Access and Contactless Mobile apps have become integral to modern parking systems. These apps allow users to access parking facilities via mobile-based credentials, providing a highly user-friendly solution. Additionally, the inclusion of contactless functionality ensures a smooth and secure experience by enabling proximity-based access, where users don’t need to physically touch any devices. This system is becoming increasingly popular for its convenience, especially for short-term and transient users. Advantages of Automated Parking Access Systems Automated parking lot access solutions offer several advantages over traditional methods, making them a smart investment for facility owners: Enhanced Operational Efficiency By replacing manual processes with automated systems, parking facilities can streamline operations, reduce wait times, and eliminate bottlenecks at entry and exit points. Cost Reduction Automation minimizes the need for on-site staff, lowering payroll expenses. Machines efficiently handle ticketing, traffic direction, and payment collection. Increased Revenue Integrity Automated systems reduce revenue leakage by preventing employee-related thefts and mitigating errors in manual transactions. Comprehensive Data Insights Automated systems maintain detailed records of all transactions, offering valuable data for analytics. Facility owners can use this information to identify trends, optimize parking capacity, and enhance decision-making. Improved Security Advanced access control mechanisms like LPR and RFID technology ensure that only authorized vehicles gain entry, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and related incidents. Choosing the Right Parking Lot Access Control System Selecting the ideal system depends on the unique needs of your parking facility. Factors to consider include: User Base: Assess whether your users are short-term visitors, long-term tenants, or a mix of both. Security Requirements: Prioritize systems like LPR or RFID for high-security locations. Ease of Use: Ensure the system is intuitive and accessible for all users, including those unfamiliar with advanced technology. Scalability: Opt for solutions that can grow with your facility’s needs, accommodating increased traffic or expanded services. By aligning your choice with these factors, you can create a tailored parking access solution that balances security, efficiency, and user satisfaction. Innovations in Parking Lot Access Control Technology The parking industry has witnessed remarkable technological advancements in recent years. These innovations aim to enhance the user experience, boost efficiency, and ensure sustainability: Cloud-Based Parking Management Cloud-based platforms offer centralized management of multiple parking facilities, enabling real-time monitoring and remote control. This approach enhances scalability and reduces the need for on-site infrastructure. Smart Sensors Smart sensors embedded in parking spaces detect vehicle presence, providing real-time availability updates to users via mobile apps. This feature reduces the time spent searching for parking spots. Mobile Integration Mobile apps have become integral to modern parking systems, offering features such as digital payments, navigation to available spaces, and reservation management. Renewable Energy Solutions Sustainable parking facilities now integrate renewable energy sources like solar panels to power access control systems, lighting, and EV charging stations. Advanced Analytics Data analytics tools analyze parking patterns, helping facility owners optimize space usage and implement dynamic pricing models to maximize revenue. Real-Life Applications of Parking Access Control Systems Parking access control systems are deployed across various sectors, demonstrating their versatility and impact: Corporate Offices Automated systems streamline employee parking, reducing entry times and minimizing delays. Advanced features like LPR ensure secure access for registered users. Residential Complexes Secure access control mechanisms, such as keypads or phone recognition, offer convenience and safety for residents and visitors alike. Commercial Parking Lots Dynamic systems handle high traffic volumes efficiently, incorporating automated ticketing and payment solutions to optimize operations. Healthcare Facilities Hospitals and clinics benefit from smart parking systems that prioritize patient and staff access while accommodating emergency vehicles. Educational Institutions Universities use automated parking solutions to manage large student and staff populations, ensuring organized and secure parking facilities. Future Trends in Parking Lot Access Control As urbanization and technology
Elevator Access Control Simplified: A Comprehensive Guide
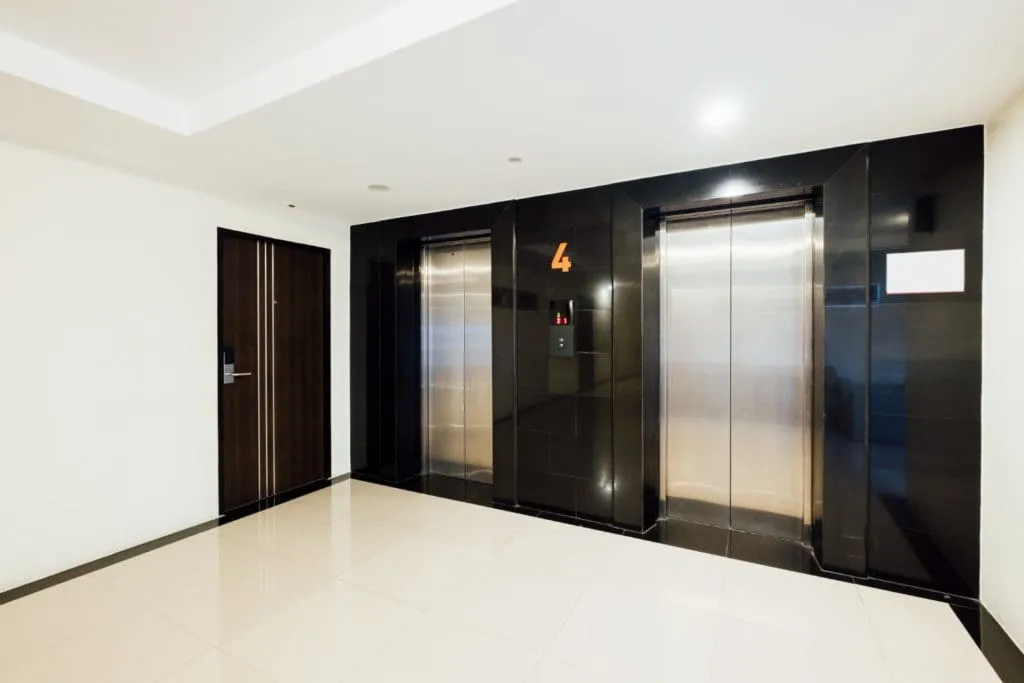

Updated on December 9, 2024 In modern building management, elevator access control has become essential to secure and restrict movement within multi-floor facilities. Unlike conventional access control, where authorized users simply open doors, elevator access control directs movement through multiple building levels, limiting floor access to only those permitted. This guide delves into the mechanics of elevator access control, including how it works, types of systems, credentials, configurations, security challenges, and evolving cloud-based technologies. With this knowledge, building managers and property owners can elevate their security measures to enhance building convenience and safety. Deciphering the Functionality: An elevator access control system relies on three main components: Elevator Control Buttons: Used to open and close doors, make emergency calls, and select floors. Access Readers: These devices, using RFID, keypads, or biometric scanners, verify that users have the proper credentials to access specific floors. Access Control Panel: This control hub manages user data and permissions, typically as an on-site server or through a cloud-based solution. Together, these components ensure that only authorized personnel can access certain floors, promoting security and safety in sensitive areas like office buildings, medical facilities, or high-rise residential complexes. Streamlined Usage Instructions Using elevator access control is straightforward. Upon entering the elevator, a user presents their credential—be it a keycard, mobile phone, PIN, biometric scan, or one-time code. If authorized, the system allows the elevator to move to the designated floor. Unauthorized users will be restricted from selecting or accessing restricted floors. Types of Elevator Access Control Credentials To accommodate various security needs and user preferences, elevator access systems support different types of credentials: Mobile Credentials: Allows users to access floors by tapping a mobile device, reducing the need for physical keys or cards. Keycards, Fobs, or Badges: The most common credentials, these provide reliable access when swiped or tapped. PIN or Passcode: Ideal for temporary or multi-user access, users enter a code to gain access to specific floors. One-Time Code: This credential type is ideal for one-time visitors, such as deliveries, allowing managers to provide a temporary access code that expires after use. Biometric Access: Uses unique user data, like fingerprints or facial recognition, to ensure high-security access. Configurations of Elevator Access Control Systems Elevator access control can be customized to fit specific building needs. Here are four common configurations: Private Elevator for General Access: Users require authorization to summon the elevator but can access any floor freely once inside. Public Elevator with Restricted Floor Access: The elevator can be called without restrictions, but access to certain floors requires credentials. Private Elevator with Selective Floor Access: Users need authorization both to call the elevator and to access specific floors. Destination Control System (DCS): This advanced system allows users to select their destination on an external panel, which optimizes elevator usage based on the scanned credential, directing users to specific elevators. The Rise of Cloud-Based Elevator Access Control With remote work and evolving security needs, cloud-based access control systems are gaining popularity. These systems allow remote management and monitoring, making them ideal for multi-location building owners and property managers. They also support seamless updates and scalability, adapting easily as buildings add new floors or tenants. Popular Cloud-Based Options Include: Single Elevator Access Control: A cost-effective solution for small buildings or residences. Elevator Banks: Suited for high-rise commercial buildings where multiple elevators serve various floors. Smart Elevators: Integrates multiple elevators into a centralized system, ideal for office towers where efficient elevator use is essential. Expanded Security Enhancements Modern elevator access control systems offer enhanced features to ensure both convenience and heightened security: Time-Based Access Permissions: Limits floor access to specific hours, suitable for facilities with restricted visiting hours. User Logging and Reporting: Tracks access attempts and movements, providing insights for security audits. Anti-Passback Technology: Ensures credentials can’t be reused immediately, reducing the risk of “tailgating” unauthorized entry. Integration with CCTV: Pairs elevator access logs with real-time video, allowing security teams to monitor and respond to potential threats efficiently. Detailed Challenges and Solutions in Elevator Access Control Elevator access control faces unique challenges due to frequent public use and the potential for security lapses. Here’s a look at some common issues and solutions: Tailgating: One of the most common issues, tailgating involves unauthorized individuals entering behind an authorized user. Anti-tailgating technology and clear user guidelines can help mitigate this risk. System Failures: Elevator access systems must remain operational even during power outages or software failures. Back-up power sources and fail-safe protocols can keep elevators running in an emergency, ensuring user safety. Credential Security: Lost or stolen credentials, like cards or mobile devices, can compromise security. Multi-factor authentication and biometric credentials offer additional protection by tying access to a user’s unique characteristics. Technological Advancements in Elevator Access Control In the ever-evolving landscape of building security, modern elevator access control systems integrate cutting-edge technologies to help overcome common security challenges. Here’s how these systems integrate with other technologies to enhance reliability and security: Mobile Access Control Integration: Mobile access control systems enable building managers to remotely grant access to elevators using mobile devices. This capability is especially useful in managing visitor access and responding to emergencies quickly, all without the need for physical presence on-site. Video-Based Analytics Integration: Advanced access control systems integrate seamlessly with video surveillance, using video-based analytics to detect unusual behavior patterns near elevators. By analyzing real-time footage, the system can identify potential security threats, alerting personnel to suspicious activities, and allowing for quicker response times. This integration also allows for footage to be linked directly to specific access events, simplifying the process of security review and incident management. Tenant Management Module: Access control systems offer robust tenant management features, enabling multi-tenant buildings to customize and streamline access for each tenant. This module ensures that tenants can only access floors or areas relevant to their needs, minimizing security risks and ensuring that authorized personnel have controlled access across different building levels. Visitor Management Module: A visitor management module integrated with the
Mobile Access Control: What are Mobile Credentials?
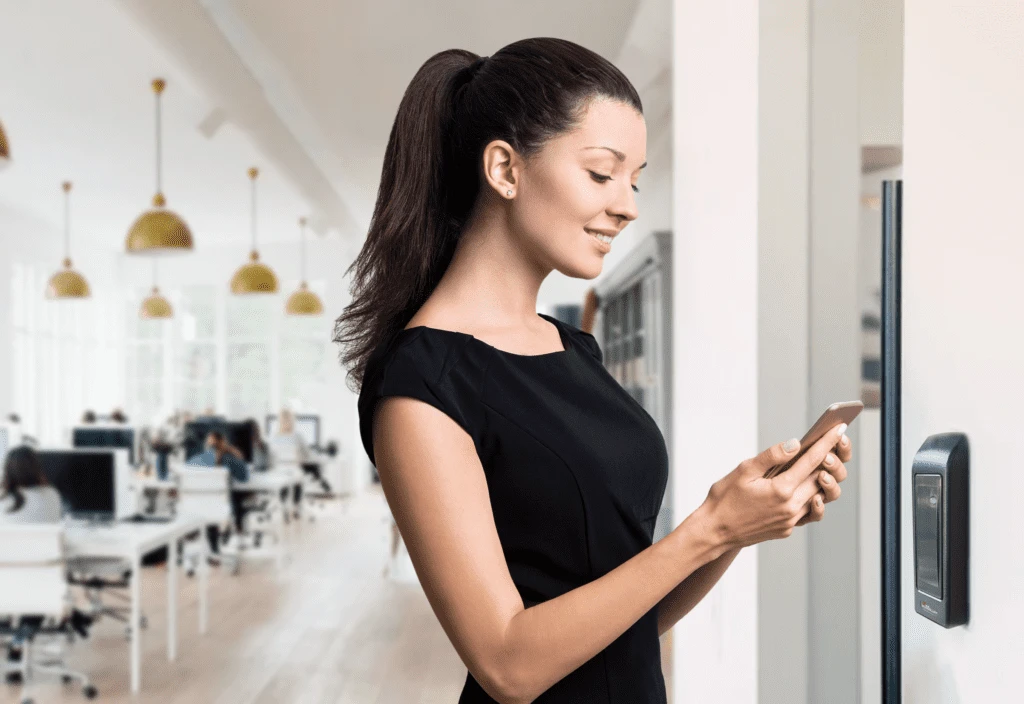

A mobile access control system enables smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches to serve as digital keys, providing convenient, secure access to restricted areas. This technology is rapidly transforming the access control industry, offering a more efficient and flexible solution compared to traditional keycards, fobs, and badges. With the rise of IoT and smartphones, mobile access control is becoming a preferred choice for organizations worldwide, as illustrated by a Gartner report stating that 20% of organizations have transitioned from physical to mobile credentials What is a Mobile Access Control System? Mobile access control replaces physical access methods with digital credentials stored on mobile devices, allowing secure access through Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Near Field Communication (NFC), and cloud-based remote access. By integrating these technologies, the system allows proximity-based access through secure connections between the reader and the mobile device. For additional convenience, many systems also allow remote access. This feature enables users to unlock doors from any location via a mobile app, ideal for granting access to remote employees, temporary workers, or visitors without requiring physical presence at the site. The accessibility and flexibility of this feature significantly expands use cases for mobile access control, particularly in larger buildings and geographically dispersed facilities. How Does a Mobile Access Control System Work? A mobile access control system has five core components similar to traditional access systems: access points, personal credentials, readers, control panels, and access servers. However, instead of relying on physical cards, mobile access control uses digital credentials stored on smartphones. By integrating BLE and NFC technology, the system allows proximity-based access through secure connections between the reader and the mobile device. Mobile access systems can also leverage cloud-based remote access, allowing administrators to grant or revoke access from anywhere, making it a convenient solution for managing multi-site operations or providing temporary access. The Advantages of Mobile Credentials Superior Security Measures Mobile credentials are more secure than traditional keycards and fobs. Key security benefits include: Unclonable Devices: Unlike physical cards, smartphones cannot be cloned, drastically reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Built-in Security Features: Mobile devices offer built-in security, including passcodes, fingerprint scanning, and facial recognition, adding multiple layers of protection. Two-Factor Authentication: High-security areas can implement two-factor authentication by requiring users to unlock their phones with biometric identification before access. End-to-End Encryption: Mobile access control systems offer encrypted communication between devices and access points, ensuring secure data transmission. Enhanced Convenience for Users and Administrators Mobile credentials streamline access management by eliminating the need to carry physical access cards. Users can rely on their smartphones for entry, which are less likely to be forgotten or misplaced compared to traditional credentials. Here are key convenience benefits: Hands-Free Access: BLE-enabled mobile access control systems allow users to gain entry simply by approaching the reader, removing the need for manual interaction. Motion-Activated Entry: Some mobile readers offer motion-activated “Wave to Unlock” features, enabling touchless access. Remote Unlocking: Through cloud connectivity, authorized users or administrators can remotely grant or revoke access, making mobile credentials an ideal solution for multi-site management. Cost-Effectiveness and Operational Efficiency (Enhanced Content) A mobile access control system reduces the long-term costs associated with traditional physical access control. Key cost-saving features include: No Physical Credential Expenses: Mobile credentials eliminate the need for purchasing and managing physical cards, fobs, or badges, leading to lower overhead costs. Cloud-Based Management: Mobile access systems often use cloud storage for credential management, eliminating the need for on-premises servers and reducing maintenance expenses. Minimal Hardware Investment: Since most employees already have smartphones, organizations can skip the cost of issuing dedicated hardware, making mobile access highly cost-effective. Types of Mobile Access Control System Technology Mobile access control utilizes several key technologies to enable secure and convenient access. Here’s an overview of each technology and its applications: 1. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) BLE technology enables devices to communicate over relatively long distances, allowing users to access buildings hands-free. BLE-based systems typically connect to readers without manual pairing, making access seamless and user-friendly. 2. Near Field Communication (NFC) NFC enables close-range communication between the reader and the mobile device, requiring a tap on the reader to gain entry. This method is especially popular in high-security applications where controlled, intentional access is a priority. 3. Cloud-Based Remote Access (New Content) Many advanced mobile access systems now support remote unlocking through cloud-based connections, allowing users or administrators to grant access from anywhere. This feature has become increasingly relevant in today’s hybrid and distributed work environments, where remote management is essential for security and convenience. Mobile Access Control System: A Safer and Smarter Solution Research suggests that around 74% of Americans feel uneasy without their phone. This statistic highlights a key advantage of mobile access control—users are unlikely to forget or lose their mobile credentials, as they are always with them. This level of reliability means that security teams are more likely to be notified if a phone is lost or stolen, enabling rapid deactivation of mobile credentials to prevent unauthorized access. In comparison, 17% of physical credential users lose at least one keycard or fob every year. These lost credentials can lead to significant security risks, including potential breaches and unauthorized access. By upgrading to a mobile access control system, organizations can ensure that lost or stolen credentials are immediately revoked, minimizing the vulnerability that comes with physical keys or fobs. Why Mobile Access Control is the Future of Security The shift towards mobile access control aligns with broader trends in workplace security and digital transformation. Organizations are increasingly looking for flexible, future-proof access solutions that can adapt to changing operational needs. As cloud technology, IoT, and mobile device usage continue to evolve, mobile access control systems are uniquely positioned to offer enhanced security, convenience, and cost savings. Mobile access control also integrates seamlessly with other security technologies, such as video surveillance and IoT-based security sensors. By consolidating multiple security functions within a single ecosystem, organizations can gain a more holistic view of their security
All you Need to Know About Access Control System – A Complete Guide
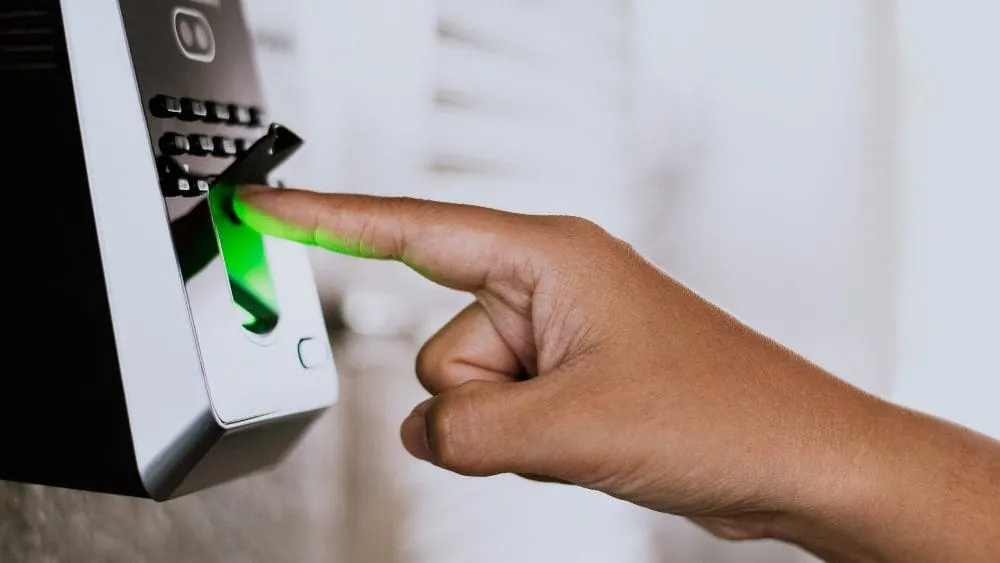

Access control systems are electronic systems that give mechanized security designated spots inside actual areas, like entryways and doors. Via automating designated spots, access control systems diminish the requirement for security staff inside an activity.
Why Is Millennium Ultra Considered One Of The Best Security Systems In The USA?

Millennium Ultra Software has been hailed as a comprehensive and robust door security system in the USA by many experts and end-users.